County File: Lancashire are finally in full bloom after more than 150 years

This is part eight of Scyld Berry's life and times of county cricket series. You can read the rest of the series here
It has taken more than 150 years for the Red Rose to achieve full bloom. Now it has, England’s supporters as well as Lancashire’s should be grateful.
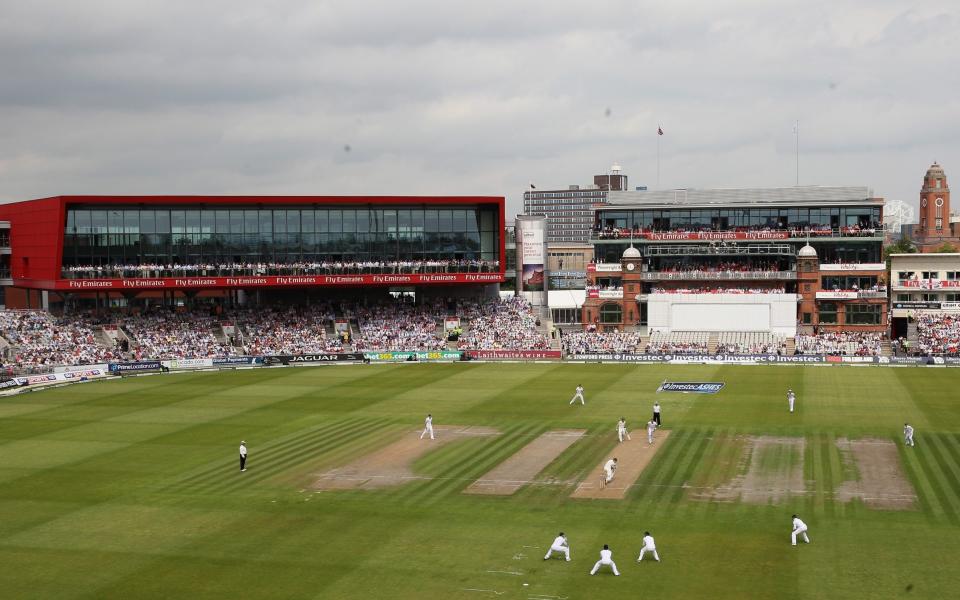
Only Lord’s has hosted three Tests before in one English summer, back in 1912, when the Triangular Tournament between Australia, England and South Africa was staged. Emirates Old Trafford is set to host three Tests this season, or what there is left of it after Covid-19.
Three Tests while none is played at Lord’s! The capital, or epicentre, of English cricket has never moved outside London before, not even in the two World Wars, but it will now as Old Trafford and the Ageas Bowl in Southampton become England’s venues. “We can comfortably find pitches for three Tests and six ODIs,” says Lancashire’s director of cricket, the former Test bowler Paul Allott. Decent pitches too: nobody wants to wait all winter and half the summer to see teams dismissed for 160.
So it is just as well the Red Rose has fully bloomed at last. There have been three periods when it has budded promisingly: in the late 1920s when they won the county championship four times in five seasons, and in the early 1970s and the 1990s when they were frequently limited-overs champions. But only now is the whole of Lancashire pulling together, taking cricket in the north-west region with it.
Lancashire alone can rival Surrey for wealth. Lancashire, indeed, make more money from non-cricket activities than any other county. But then there has always been money in Manchester: where there’s muck, there’s brass. No, it was not for lack of expensive fertiliser in times past that the Red Rose failed to bloom.
Lancashire made an unprecedented profit in 2019 - the only year when England has staged a World Cup and a five-Test Ashes series (four Tests in 1975). They had a record turnover of £34m, and made a record net profit of £5m, according to the accounts published last week.
At Old Trafford Lancashire CCC have usually been the poor relations, but not last summer, not when the World Cup qualifying match between India and Pakistan was staged. The number of millionaires who wanted to see, and be seen, made a Manchester United game look like a kids’ kickaround in the park. On the morning of that qualifier, tickets were being touted for a thousand quid. So many private jets flew in from India, America and the Gulf that Manchester Airport could not accommodate them all and had to divert some to Liverpool.
Old Trafford was entrusted with the World Cup semi-final too, when New Zealand’s pace bowlers overwhelmed India’s batsmen, habituated to flatter pitches. The carry which Old Trafford had before the square was realigned a decade ago has gone, and the pitches are simply quicker than most, but there was still enough life and lift for India to crumble to five for three. The jets did not linger for the final.
The ground which hosted most World Cup matches last summer was Old Trafford with six - and talking of six, England hit 25 sixes in their qualifier against Afghanistan, Eoin Morgan 17 of them. It can cope with capacity crowds as well as any cricket ground in England except perhaps Trent Bridge (a two-carriage Metro tram into the city centre at close of play does not suffice). Not that this big-match experience will be vital when England host West Indies and Pakistan behind closed doors. This year there is no need to erect what the county believes to be the biggest temporary stand in Europe, accommodating 9000 spectators.
I would like every county ground to be multi-purpose, and therefore alive all year round, drawing people into gyms or sports shops or cafes under the stands. Lancashire made their record profit last year largely because they have gone further down this route than any other county. The combined turnover of the Hilton Garden Hotel, with 150 bedrooms inside the ground and run by Lancashire, and the red-roofed Point - which can accommodate 1200 people for conferences, meetings and weddings - was £9m.
Hardly less important, the ground’s redevelopment works architecturally. Adding a tier to the old pavilion and blending it in with the top of the Point has renovated the old Victorian structure and given the ground its own identity, in red. Like Lancashire CCC, the pavilion has had many ups and downs over the years, but finally grown into a synthesis of ancient and modern.

When Old Trafford’s cricket ground stages a concert, it can host 50,000 spectators and generate a profit of about a quarter of a million: but no concert last year, which was too busy with cricket, because pop-concert fans can churn up the outfield. The ample car park facilities bring in another £300,000 year-round and especially when Man Utd play at home. Lancashire used to have a No 2 ground or nursery on the site where the nets and some car parking spaces are.
Given all this brass, Lancashire, like Surrey, did not have to put their players on furlough as every other county did. “In essence we want to keep in touch with them,” says Allott. “They’ve got equipment for training at home and this way our physiotherapist and nutritionist can work with them - and we’ve got our sports psychologist on-call 24 hours. Liverpool have also started to use Lee Richardson, since Jurgen (Klopp) heard about him.”
“We are trying to maintain contact with our members (almost 5000, who generate about half a million pounds), sponsors and stakeholders. The players are offering training and coaching tips on line, and doing Q and As for under-10s upwards. I find the value we get from that outweighs the value we get from furloughing them, for the time being at any rate,” Allott says. Including Emirates, the club’s sponsors - with the players making them feel in touch - are still putting in £2m a year.
About £34m is some turn-over for any cricket club, and some turn-round as well. “In 2010 we were within ten bob of going bust,” says Allott. Or as the chief executive Daniel Gidney explains (not that he worked at the club before the crisis): “There was a perfect storm, in that we had the global recession in 2008, and our loss of Test match status, and our £60m redevelopment of the ground was opposed by another developer, which cost us a million pounds in legal fees.” Fortunately the court found in Lancashire’s favour.
There are two sides to the coin of being the county with the highest revenue from non-cricket activities in normal years: the other side is that this year they will make little or nothing from conferencing and weddings. Smaller counties without a Test ground do not make much profit normally - and won’t make huge losses during this storm.
Three Tests this summer will consolidate Old Trafford’s position as the ground that has staged the fifth most Tests worldwide. Lord’s come first with 139 Tests, followed by Melbourne, Sydney and the Oval, all with more than 100. Old Trafford has currently staged 79 Tests, one more than Headingley - and being one step ahead of Yorkshire has always been a prime consideration during Lancashire’s existence.
Old Trafford holds the world record for having the most Tests abandoned without a ball being bowled: two, in 1890 and 1938. There would be only one fate in cricket more cruel than being locked inside Old Trafford for the best part of a week before a Test, then for the whole of the Test to be washed out without a ball being bowled. The only worse fate? The same thing happening at the Ageas Bowl.
Lancashire's origins as a gentleman's club
To understand what Lancashire was like when the county club was formed in 1864 - and one reason why it took so long to get from square one to their present fulfilment - there is no better place to start than “Cranford”.
Elizabeth Gaskell’s novel captures Manchester a decade earlier, in the early 1850s. Before the heroine finds herself a rich mill-owner, she leads us through the cobbled streets of the Industrial Revolution at its most inhumane. English factory-workers live in abject grime and poverty, and Irish workers - brought in to under-cut the wages of the English workers - exist in even worse conditions. Nobody in such a society is going to have any time or wherewithal to watch or play cricket, except the mill-owning elite.
So when Lancashire CCC was formed, in the mid-Victorian splendour of the Queen’s hotel in central Manchester in 1864, it was a gentleman’s club: not an organisation dedicated to spreading the sport around the county or winning matches, but a gentleman’s club.
“There are cheap jokes about Manchester’s weather; ‘Cottonopolis’ is a jibe, and there are slums and smoke enough, but Manchester is the home of the Manchester Guardian, of the Halle concerts, of a repertory company which made its influence felt throughout the country… in addition to producing some of the great political figures of the C19th,” wrote Dudley Carew in ‘To The Wicket’. “There are clubs in Manchester where the talk is wittier and better informed than in the corresponding clubs in London. Old Trafford is the expression of this comfortable, cultured tradition.”
In seven of Lancashire’s first eight games, no professionals were selected for this gentlemen’s club, and when they were, they soon knew their place. According to Stephen Chalke in his definitive work on the county championship, ‘Summer’s Crown’: Lancashire’s professionals “were kept in place, being allocated a ‘cow shed’ in which to change and eat their own packed lunches.”
The man who did most to shape Lancashire was the son of a cotton mill-owner who was MP for Blackburn: Albert Hornby, whose son ruled Old Trafford for almost as long. When the myth of the Ashes was generated at the Oval in 1882, Hornby was England’s captain as they lost by seven runs, and therefore the man ultimately responsible for the strategy of not playing shots as England failed to chase down their target of 85. He was captain again when England played their first Test in England away from the Oval, at Old Trafford in 1884: but then the home county committee selected the England team, not MCC or independent selectors, so they would choose Hornby, wouldn’t they? He did not rise to the occasion, becoming the first batsman to be stumped in both innings of a Test, for 0 and 4.
At county level Hornby could bat alright, and scored the first seven centuries for Lancashire, and led them to their first championship titles in 1881 and 1897. He also became the first man to captain England at cricket and rugby, which was a little strange - strange because he was so little. When he was in the Harrow Ist XI, he weighed less than six stone while holding his bat; and his nickname was “Monkey”, which might have been inspired by the parting of his hair down the middle as well as his size and simian agility. Lancashire’s professionals did not address him as “Monkey” but “the Boss.”
It seems amazing now that one so slight should have played full-back for England, but that was before All Black forwards had to be tackled. Hornby was in England’s XV for the first rugby international, against Ireland in 1877, and was captain when they lost in Manchester to Scotland in 1882, so in neither sport was his captaincy very successful. “Small, truculent, bellicose, adventurous, rash and a poor runner between wickets,” was Christopher Martin-Jenkins’ verdict on Hornby, which was scathing by his standards. Hornby, however, did inspire the poet Francis Thompson to write immortal lines on Hornby and Richard Barlow batting together, when “the run-stealers flicker to and fro, to and fro.”
A whole century later, by the early 1960s, Lancashire were as hierarchical - or feudal - as ever. David Lloyd, in his entertaining autobiography, says that the place where junior professionals changed was called “the Dogs Home”, not much improvement on a cowshed. He recalls “an ‘Upstairs, Downstairs’ divide, in which the young players were expected to be cringingly subordinate to their seniors.”
Club members - gentlemen - could still stroll down to the nets and have the professionals bowl at them, gently. The county was still captained by an amateur. In 1962 an Old Reptonian was appointed, Joe Blackledge, who had never played first-class cricket before, after the captaincy had been advertised in The Times. Appearances, and class distinctions, were what mattered, not results. A structure of committees and sub-committees aggravated matters: the general committee sacked two senior players, then the members sacked the committee. Before 1960 Lancashire seldom finished outside the top six in the county championship; from 1961 to 1969 they finished once in a single-digit place.
The Golden Era of the Lancashire Leagues
Everyone in those days was pulling in different directions. League cricket was always threatening to siphon off those cricketers who wanted to play less than six days a week, or for more money. The great days extended into the 1950s, when Lancashire league clubs employed the very finest West Indian cricketers, from the 3 Ws and Garfield Sobers to Wes Hall and Sonny Ramadhin. Why go to Old Trafford, to get bored and rained on and watch a draw (and Lancashire have drawn more championship matches than any other county), when you could watch world class down the road, and a result on the day?
Lancashire lost the world’s best-ever bowler - you could still argue - to league cricket. Syd Barnes, who bowled quick leg-spin mixed with offbreaks, and took 189 Test wickets at 16 each, played two seasons for Lancashire at the start of the C20th, then spent the rest of his career in leagues, where he could earn more money for longer. His accountant surely approved when Barnes, aged 56, was still rated the best bowler in England.
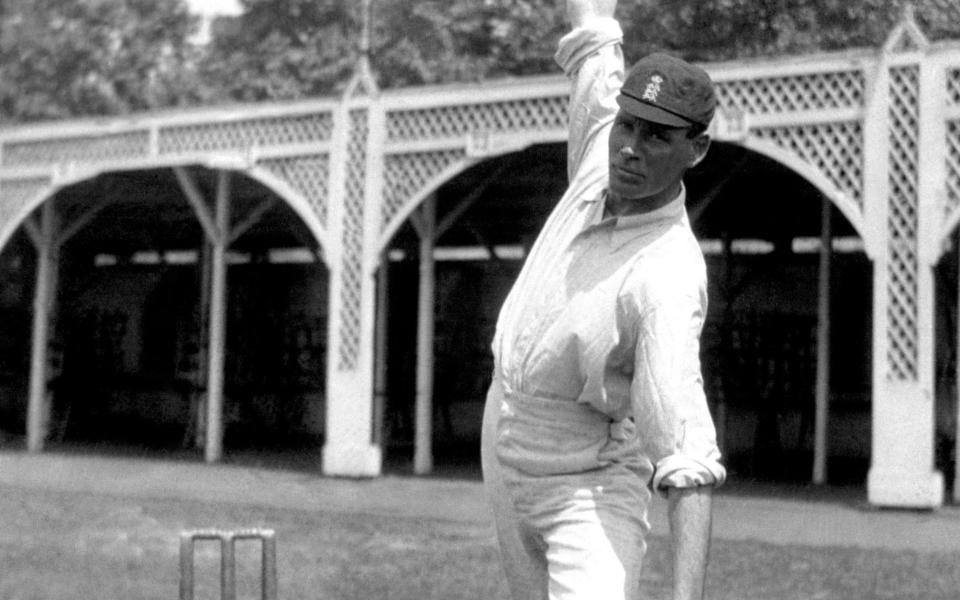

The impact of League cricket on Lancashire CCC was summed up by Hon Terence Prittie when he filled in as the Manchester Guardian’s cricket correspondent in 1946. “The financial lures of the Lancashire and Central Lancashire Leagues had hit the county very hard. Eddie Paynter had left them” (after averaging 59 for England) - along with another England batsman, Norman Oldfield. “Lancashire’s troubles did not end there. Farrimond, their international wicketkeeper, and Nutter, who should have been an England allrounder of the near future, migrated to the Leagues too.” Allrounders would fare especially well in league cricket, because a collection would be made for anyone who scored 50 or took five wickets. Given crowds of two or three thousand, that was a lot of threepenny bits to supplement their salary.
Lancashire’s response to their crisis in 1946? Appoint an amateur captain who had never played before, of course. John Fallows, as captain and specialist batsman in 1946, averaged 8.14, then retired.
The best overseas signing of them all?
Still, there was enough brass to enable Lancashire to become the first county to win a hat-trick of titles in two formats, by bringing in overseas players to make the difference. The first was Ted Macdonald, who spearheaded Lancashire’s hat-trick of championship wins from 1926 to 1928. He was paid £500 a year, then the biggest salary in cricket, more than Sir Jack Hobbs at Surrey, and almost as much as WG Grace used to rake in as an amateur.
Jimmy Anderson, Brian Statham, and Macdonald, who was born in Tasmania: Lancashire has been home to three of the finest pace bowlers. Extreme flexibility is something they had in common: so athletic that they could warm up with a fag and a pint while others slaved in the nets, and so fit they were all at their best in their 30s not 20s. Of the three, Anderson swung it the most, while Statham and Macdonald tended to seam the ball into righthanders. Anderson and Statham never bowled a bad ball and were remorselessly accurate; but don’t think Macdonald was the least of them just because he played so long ago.
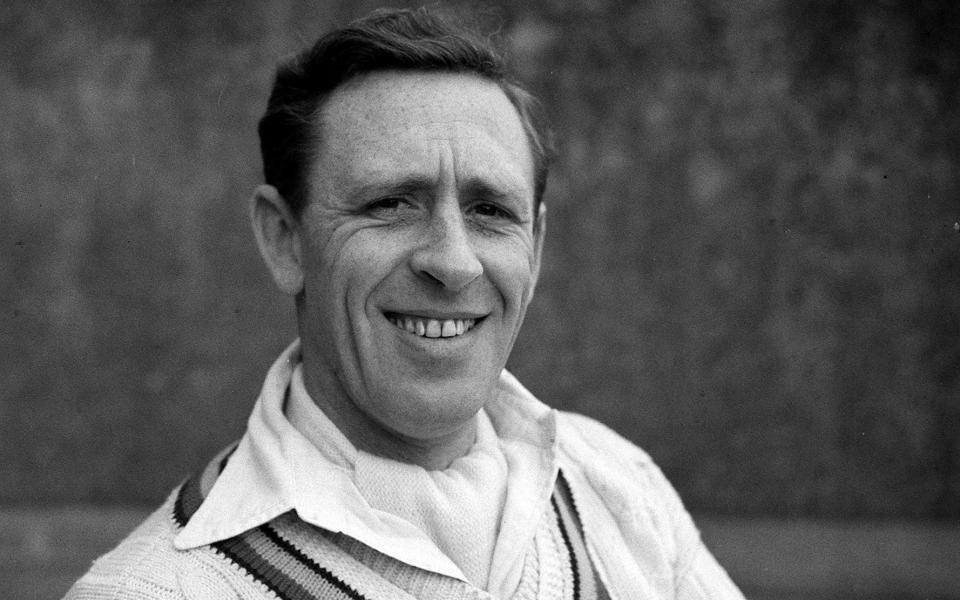

We have the word of Sir Neville Cardus that Macdonald, for the first ball of Kent’s second innings against Lancashire at Old Trafford in 1928, bowled a short ball that flew over the batsman and keeper, or “crashed halfway along the pitch and then hurled itself high over the heads of the batsman and Duckworth. Whence does Macdonald draw his terrible strength and velocity? His run to the wicket is so easy, so silent.” Anybody who can run in, without warming up, and bounce his first ball over batsman and keeper is sharp.
Mike Procter, Bruce Dooland, Clive Lloyd, Ken McEwan, Viv Richards, Simon Harmer? Economists can probably calculate who was the most valuable - the most rewarding - of all overseas players; but it could well be Macdonald, as he won the championship - the only format going - four times for Lancashire in six and a half seasons, and took 1053 wickets at 20 runs each when Old Trafford was a belter.
Having toured England with Australia in 1921, and terrified English batsmen, Macdonald had signed for Nelson for £500 a year plus bonuses. In 1925 Lancashire lured him for the same salary, and a house, and the promise of a benefit after only five years (£1947 in 1929): he needed the money, to pay his gambling debts in horse-racing. As a league pro, Macdonald learned to bowl offcutters as well as flat out, and delivered well over 1000 overs per year for Lancashire.
So Lancashire were the champion county when they harnessed Macdonald’s pace to their strong, but very defensive, batting line-up. For truth be told, or at least if Cardus is to be believed, never did any county bat so dourly. Other critics agreed: “There was a time in the ‘twenties when the cricket they played set a deplorable standard other counties were all too willing to copy,” Carew wrote, as a cricket correspondent for The Times. “Time and again it seemed that Lancashire, with Hallows and Watson to start them off, went into the field with the negative intention of not losing the match” - in the Roses match above all. Eight consecutive championship matches between Yorkshire and Lancashire in four years in the late 1920s were drawn; over half of all Roses matches in all.
“Day after day columns of indignation, coloured with all of “Cricketer’s” charm and dramatic indignation, spilled themselves over the Manchester Guardian. Lancashire was denounced with the fire and wit of Disraeli,” Carew wrote of Cardus. But the wittiest, most incisive criticism which Cardus levelled at Lancashire’s batsmen came in his Autobiography, that flawless work of prose, which schoolchildren in India would be given for their English exams. You recall: “Illustrate the author’s use of adjectives/adverbs in this passage.”
Cardus was married during the 1921 cricket season during one of Lancashire’s home matches. “I went as usual to Old Trafford, stayed for a while and saw Hallows and Makepeace come forth to bat. As usual they opened with care. Then I had to leave, had to take a taxi to Manchester, there to be joined in wedlock at a registry office. Then I - that is, we - returned to Old Trafford. While I had been away from the match and had committed the most responsible and irrevocable act in mortal man’s life, Lancashire had increased their total by exactly seventeen - Makepeace 5, Hallows 11, and one leg-bye.”
Yet the dullest cricket inspired the most luminous of all cricket prose. “In a representative Lancashire and Yorkshire match of 1924-1934, runs were severely discountenanced,” Cardus wrote. “No fours before lunch, on principle, was the unannounced policy; and as few as possible after. But fours or no fours, runs or no runs, the games touched greatness because of the North of England character that was exposed in every action, every movement, all day.”
So far away in terms of time, yet so near. The Roses match in the championship has, for many recent years, been played behind virtually closed doors, but the T20 Roses match packs in a full house, just like a century ago. The consumption of alcohol now might be slightly greater but singing used to be a feature of cricket at Old Trafford in the late Victorian and Edwardian eras, not least when it was raining: spectators went there for a day out and kept their spirits up.
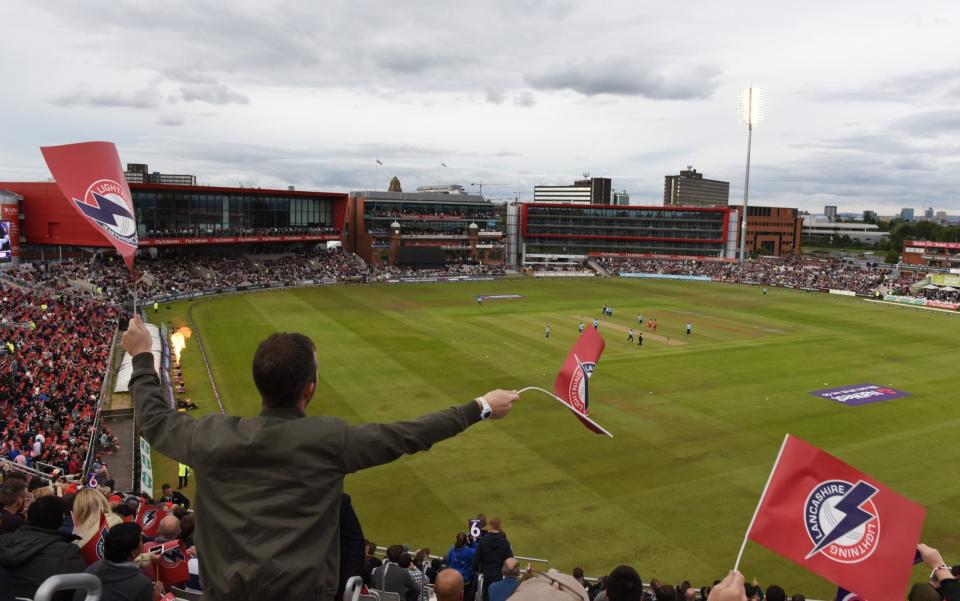

The T20 Roses Match of 2018 at Old Trafford, in front of a capacity crowd, was as entertaining as any cricket match of such a length could be. Rain reduced it to 14 overs a side. Lancashire scored 176 for two, Liam Livingstone hitting 79 off 37 balls (why did England’s selectors encourage him to bowl white-ball offspin when he could have been an England Test number six bowling legspin?). Yorkshire replied with 175 for four, losing by one run. Had Cardus nipped out to get married during that game, he would have missed more than 17 runs, because sometimes that was scored off one over.
Limited-overs success came in the 1970s
It was the signing of Clive Lloyd of West Indies, and Farokh Engineer of India, that sparked the first hat-trick of titles in a limited-overs format: the Gillette Cups of 1970-72, under the captaincy of Jack Bond. Lancashire had already come close, by winning the first two Sunday Leagues in 1969 and 1970.
Lloyd, or “Hubert”, was an electrifying lefthanded batsman, an electrifying fielder before his knees went, and was taken to Lancastrian hearts (attitudes had changed since the 1930s when the West Indian Learie Constantine was rejected as Macdonald’s successor). Sir Clive was knighted in the New Year honours list of 2020.

Engineer was ahead of his time in being a wicketkeeper who could not simply bat but open the batting and hit. He brought flash and panache to a defensive era in Indian as well as Lancastrian cricket. He was part of the last flowering of Parsi cricket in the early 1960s, when their tiny community supplied four regular members of the Indian Test team.
“The start of the Sunday League offered a challenge that was right up our street,” wrote the other Lloyd, David, who opened the batting with Engineer. “Most of us had come through the leagues and were accustomed to playing overs cricket in a single afternoon. While certain other counties floundered in the environment, or failed to identify its potential, we took to it immediately.” Lancasheer la, la, la. Lancasheer la, la, la!
The only drawback was that Lancashire specialised in the limited-overs formats; they took their eye off the red ball. They went on to win eight one-day trophies in the 1990s; but the championship - last won outright in 1934, shared in 1950 - was as elusive as ever. It was 2011, when Old Trafford was closed for renovation, and Lancashire played their home games at Liverpool and other out-grounds with result pitches, that all the petals of the red rose began to flower. When they won the T20 trophy in 2015, Lancashire had the full set.
The Red Rose finally in flower
The first known person of note in English cricket to die of coronavirus was David Hodgkiss, Lancashire’s chairman. He had attended the last big sporting event before the lock-down, the races at Cheltenham, where he is thought to have caught it. Hodgkiss was 71. “He was a top bloke and the effect of his demise will be felt for a long time to come,” says Allott.
Or maybe, Hodgkiss’s legacy is already visible. “He was a wonderful man, who used to open the batting for Cockermouth,” says Daniel Gidney. “Whether you were a pot-washer in the catering department or an opening batsman in the first team, he had the same smile for everyone.”
Players seldom have a good and truthful word for administrators, but Hodgkiss inspired these two tributes from players past and present. “I knew him extremely well,” Engineer said. “He was the best and most popular chairman LCCC ever had.” And Matt Parkinson, the legspinner whom England are blooding, and who received his Lancashire cap from Hodgkiss, tweeted: A great man who always had time for everyone and loved the Will remember his capping speech for a long time .”
This is a world away from Lancashire’s hierarchical system which held them back for so long. Hodgkiss deserves to be remembered as the man who chaired the club - no more committees, just a small board of great and good - as they finally became the northern power-house which their resources had equipped them to become many years before.
Lancashire have long had a friendly relationship with Cheshire and they have extended it to Cumbria too. The tension with all their many leagues has disappeared, along with the Central Lancashire league itself: David Lloyd, when he joined Lancashire, was no longer permitted to play for his home club of Accrington! Nowadays Old Trafford hosts a two-day fixture between Lancashire second XI and a team of the best league players. This forms part of a pyramid leading to the top, as in every Australian state, whereas the shape of cricket in Lancashire used to be that of a blancmange.
“We are aiming to get cricket into 1000 state schools in the north-west for boys and girls,” says Gidney. Lancashire already produce 10% of all county cricketers: in other words, 10% of current players were either born in Lancashire or came through pathways within the county. Yes, this is fulfilment. The Red Rose is finally in full flower.

 Yahoo Sport
Yahoo Sport 





































