Rugby tackles above the waist banned in RFU trial
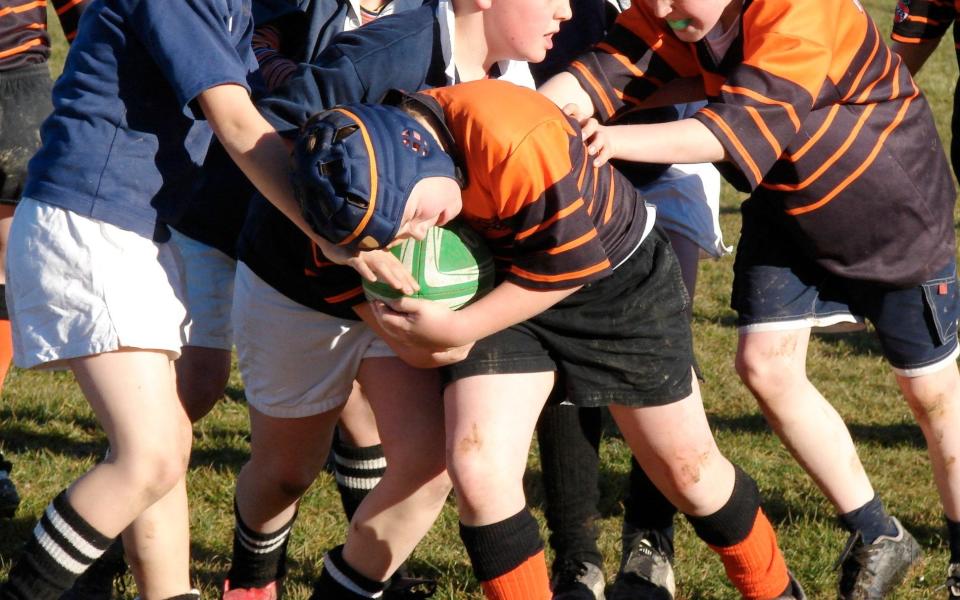

Tackles above the waist will be outlawed in some age-grade matches next season as part of a law trial by the Rugby Football Union that could increase offloads and radically alter the nature of the sport.
The initiative also aims to restrict dipping into contact from ball-carriers, in a bid to reduce head-to-head contact and prevent concussion. It will be evaluated in 1,200 club and school matches for boys and girls between under-16 and under-18 levels.
Having monitored the progress of a similar trial in France, the RFU expect there to be fewer rucks and more opportunities for passes out of contact.
Injury surveillance will be collated and video analysis will be carried out over the 2021-22 season, with matches under these laws compared to 1,200 matches under standard ones at the same age-grade.
“It’s an evidence-based, game-led approach,” said Simon Kemp, the RFU’s medical services director. “This is about head impact and concussion prevention. We know that the most effective control measures are law changes and coaching behaviour.
“What we’re doing here is taking five or six years of data analysis to develop and implement a law change supported by coach input that we anticipate will have a positive effect on injury risk.”
“Interim outcomes from the evaluation of a waist height tackle law variation in French community rugby show that a tackle at waist height or below — together with the prohibition of the ball carrier bending into contact — are having a positive impact on reducing the number of serious head impacts.
“[The laws] are viewed positively by players, coaches and referees and from the video examples provided appeared to show a change in the shape of the game, with fewer rucks and more offloads.”
“We are very excited to be evaluating a waist height tackle law variation of our own next season to see what we can learn from the data and player and coach feedback.”
Those monitoring the trial must be wary of unintended consequences. As recently as January 2019, a law trial carried out over the pool stage of the Championship Cup was abandoned. After the legal tackle mark was lowered from shoulder to armpit-level, there was a rise in concussive incidents due to collisions where both tacklers and carriers were bent at the waist.
Meanwhile, the legal tackle height for under-15 to under-18 age-groups will be lowered from the line of the shoulders to the line of the armpit.
This brings it into line with the rules for those playing full-contact rugby between under-9 and under-14 levels in a bid to ease the transition of players that have endured seasons disrupted by Covid 19.
“This is an exciting and important piece of work,” said John Lawn, the RFU’s head of game development.
“We started planning for this back in 2019 and it builds on everything done in the age-grade game over the last decade, putting in place a building-block approach to full-contact rugby.
“We want to make the game as safe as possible, but without losing the physical element that’s popular with players and this law change supports that.
“As a result of the fallow 2020-2021 season due to Covid 19, all age-grade players, except for next season’s under-17 and under-18 age grades, will only have experienced tackling below the line of the armpit. A continuation of the laws they were previously familiar with will support their reintegration back into the game.
“Maintaining a single tackle height also supports the integration of players in the dual or triple age bands in the girls’ game.”
It is early days but baby steps could lead to a very different game
By Gavin Mairs
The results of this trial could have profound implications for the game.
While the primary focus is on improving safety, the introduction of waist-high tackling in 1,200 games in the Under-16 to Under-18 age grades in England next season could also lead to a butterfly effect on how the game is played.
Data available from similar trials in France and Fiji in the community have already shown a significant decrease in the number of head impacts – 60 per cent according to French Rugby Federation statistics.
Lowering the permissible height of the tackle has the almost immediate benefit of reducing the incidence of dangerously high tackles above the neck.
But to make those gains, it seems that the body position of the ball carrier is equally important to the tackler.
In January 2019, the Rugby Football Union was forced to abandon a trial in the Championship Cup where players were not allowed to tackle above the armpit because of an increase in the number of concussions, mainly due to the fact that the ball carrier had been bent at the waist in the moment of impact.
To prevent a repetition, this new trial will also restrict “late dipping and/or leading into contact with the head” to reduce the incidence of head-on-head impacts and in turn offer greater protection to the tackler.
Interestingly, the data from France also shows that their trial has resulted in a reduction in the number of rucks, and there is a hope that in reducing the tackle height, the knock-on effect will be to create more space for the attacking side and a greater tempo.
The trend for tacklers to hit the ball-carrier higher up his body is designed in part to prevent the off-load and wrap up the ball to prevent quick release or force a turnover.
You only have to watch clips of Test matches from the 1970s and 1980s, where tackles were more often than not made at waist height to see the difference that upright tackling has made to modern-day game, where space is now at a premium.
Here the data from France is encouraging again. Stats from the trial show that not only has it become a safer game, but also had the effect of increasing the number of line-breaks (up 31 per cent), and reducing the number of kicks (down 67 per cent). Interestingly, there has also been a significant reduction in the winning margins.
It is still early days, of course, but as Simon Kemp, the RFU’s medical services director, states, it is founded on an evidence-based and game-led approach.
And if it proves successful, these baby steps could lead to a very different game in the future.

 Yahoo Sport
Yahoo Sport 





































