Eight ways to fix Test cricket's uncertain future
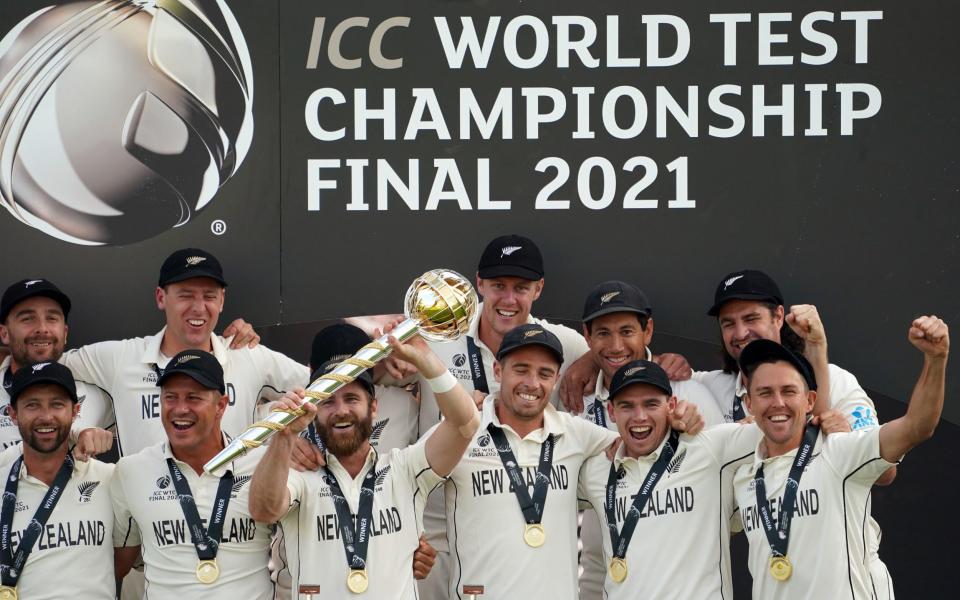

As Kane Williamson lifted the inaugural World Test Championship at the Ageas Bowl, it was a seminal moment for Test cricket. After 144 years, Test cricket, for the first time, had a winner-takes-all match to determine a world Test champion.
Yet, despite the success of the final, Test cricket’s future remains uncertain – just as it always has been. John F Kennedy said that change is the law of life; this has always been true of Test cricket. Here are eight ways to put the Test game on a surer footing.
Sort out the over rates
If Test cricket can’t solve the little things, what hope is there of solving the big ones?
No one, it is safe to assume, who attended the first day of the 2005 Edgbaston Test, when they saw England make 407 in the day, left the ground lamenting that they’d only seen 79.2 overs in the day and been ripped off.
But, too often, the over rate is lamentable even when the cricket is less thrilling. Over the first four days of the first Test against New Zealand - one of which was completely lost to rain - 21 overs were lost due to slow over rates. Such tardiness not only short-changes fans; it slows down the game on TV and, especially when there is rain, reduces the chances of a result.
Worldwide, over rates in Test cricket are now 13.7 overs an over - 30 per cent less than in the 1960s, when they were 17.7 overs an hour, according to Benedict Bermange, the Sky Sports statistician. Properly enforcing over rates should be a priority of administrators; Australia’s four point deduction on the World Test Championship table for slow over rates in the Boxing Day Test last year - which ultimately cost them a berth in the final - was a good start. Enforcing run penalties during a game would also be a far more effective deterrent than fines.
More day-night matches
Six years ago, the Adelaide Oval played host to the first ever day-night Test match. It produced compelling cricket - the difficulties of batting at twilight providing a fresh point of intrigue - and followed the simple principle of staging sport when most people can watch.
Across the world, day-night Test matches attract about 25 per cent more viewers than day Tests played. “People want to watch cricket at night - that’s when they have time,” says a senior figure in cricket broadcasting. And yet, after Adelaide’s success in 2015, just 15 of the next 234 Test matches have been day-night games.
Day-night Test matches are not needed everywhere. In England, the demand for Test matches remains vibrant; there is no need for day-night Tests during holidays - like the Boxing Day and New Year’s Tests in Australia - either. But in most situations, day-night Tests offer a simple route to attracting more fans, both in stadiums and on TV. Day-night Test matches are not a panacea for Test cricket - there isn’t one. But if day-night Tests accounted for nearer 50 per cent than 5 per cent of Tests each year, they would help to give the format the most chance to be more relevant to more people.
Improve the ball
If so much modern sport seems almost homogenised, variety is at the heart of Test cricket’s appeal. Facing England’s seamers on a cloudy day at Trent Bridge is every bit as challenging as facing India’s spinners at Ahmedabad, just in a completely different way.
But it is reasonable to ask whether one element changing from country to country enhances the game: the ball. While the Kookaburra ball is used in six of the nine nations in the World Test Championship, and the SG ball used in India, the Dukes ball - which is only used in England and the West Indies - is generally considered to provide for the best balance between bat and ball.
“The Dukes, I think, is the most suited ball for Test match cricket and if there's a situation, I would vouch for that to be used all over the world because of the consistency of the ball and how the bowlers are in the game at any stage because the seam is so hard and upright,” Virat Kohli said in 2018, shortly after India’s 4-1 series defeat in England. It is a view that Ian Bishop, the former West Indies cricketer and now a leading commentator, endorses.
“The ball for Test match cricket as far as I’m concerned must be made up like the Dukes ball. I think the other options where you have this flat seam doesn’t do much for Test match cricket when the pitches dry out. The ball is critical.”

A Netflix for cricket
In 2018, when Bangladesh and Sri Lanka toured the Caribbean, Cricket West Indies lost a total of $22million, such was the lack of commercial interest in the series. In economic terms such series are completely unviable, and rely on subsidisation from more lucrative matches - above all, hosting England and India - to survive.
Outside the biggest markets, broadcasting rights are often sold at the 11th hour, if at all, creating a confusing - and expensive - hotchpotch of channels for fans to subscribe to if they want to watch all Test cricket. Sometimes, no one buys the broadcasting rights at all: when Bangladesh drew their Test series with Australia in 2017, there was no legal way to watch the series in the UK.
The solution to these two, seemingly separate, problems might be related. Cricket boards could band together and create a Netflix for cricket, giving fans access to all matches from outside their home broadcasting market for a monthly subscription fee, borrowing from the system that Major League Baseball uses. It would be simpler for fans, perfectly designed for the smartphone age - and, by guaranteeing all boards a stream of income by pooling their broadcasting rights, help to stabilise the finances of mid-sized Test nations.
A Test Cricket Fund with teeth
The most important fact about Test cricket is that virtually all games not involving at least one of Australia, England and India - lose $400,000 in total revenue for the hosting board. This explains why New Zealand, with the best Test side in their history, can only afford to host four Test matches a year. Economic realities underpin the inequities at the heart of Test cricket - in how many games teams play, and in how much players are paid.
If Test cricket beyond the big three won’t pay for itself, it will have to be subsidised. The solution lies in restoring the Test Cricket Fund, which entailed the ICC giving cash to Test nations explicitly to pay for hosting Test cricket. More ambitiously, the ICC could also consider creating a minimum wage for Test cricket, as Jason Holder, the former West Indies captain, has advocated. Such a system would ensure that it remains in players’ economic interests to play Tests, and be an answer to the spate of players from beyond the big three shunning Test cricket because it doesn’t pay as much as franchise T20 leagues.
Nurturing new teams
Both participants at the Ageas Bowl attest to what can be gained from giving new Test nations time to grow. It took India 25 matches and 20 years to record their first Test victory, New Zealand 45 Tests and 26 years.
And so, for all the focus upon teams within the World Test Championship, Test cricket should also nurture the ‘small three’ outside the Championship who also have Test status - Afghanistan, Ireland and Zimbabwe. Since Afghanistan and Ireland gained Test status four years ago, Afghanistan have played six Tests, and Ireland just three.
To cultivate the Test game in these countries, the ICC only need look at their old model for a second division of the longest format: the Intercontinental Cup, which pitted Associate countries against each other. The ICC could relaunch the Intercontinental Cup as the second division of Test cricket. The demise of tour matches also presents an opportunity for new nations: just as Pakistan did three years ago, touring teams to England could prepare for a Test series by playing Ireland; those touring India or Pakistan could prepare by playing Afghanistan. To make them more affordable and help them fit into the schedule, such Tests could be four days.
Ideally, there would be promotion and relegation between the divisions. But - as with rugby’s Six Nations - sides are too fearful of being relegated. A compromise could be to plan to expand the number of teams in the Test Championship, perhaps eventually playing the league stages in two pools of six.
Better marketing
Who was the top scorer in the league stages of the World Test Championship? And who was the top wicket-taker? Even the players themselves might not be aware of the answers - Marnus Labuschagne and Pat Cummins.
Part of the rationale for the Test Championship is it has come in an age when fans, weaned on T20 leagues, expect every match to be part of something greater, building towards a climax. To create more of a sense of all matches being part of a greater whole, the ICC could borrow one of the IPL’s best and simplest ideas: orange and purple caps worn by the top run-scorers and wicket-takers in the competition.

A better Test Championship format?
When the World Test Championship was launched it was fashionable to decry. It was too long, too unwieldy and simply too complicated.
Those criticisms all remain valid; no one pretends that the Test Championship is perfect. But the final confirmed that the Championship marks a significant improvement over what came before: essentially, no structure.
When the Championship was created, it was never really intended to be the ultimate structure for Test cricket, but rather a first draft that could then be improved upon. While the first iteration built up to a compelling denouement, there is ample scope for the Championship to be improved upon in future editions.
There are radical options: a Test World Cup, say with two groups of four or five teams and then semi-finals and a final. Such a tournament could be played every four years - like the ODI World Cup.
Perhaps simpler would be to tweak the Championship in its current guise. The scoring system could be simplified: to three points for a series win and one for a draw, perhaps, which would be easy to understand and able to accommodate series of different length. Rather than only two out of nine competing teams making the final, adding semi-finals - perhaps played over six days, with the highest-ranked team advancing in the unlikely event of the game still being drawn - would keep more sides involved for longer and create two other high-value matches. If played in the same country as the final, they might also lead to greater interest in the final.
A game as epic and maddening as Test cricket does not lend itself to an easy format to determine the world champion. Yet the Test Championship, for all its flaws, represents the best opportunity to sustain the five-day game throughout the world.

 Yahoo Sport
Yahoo Sport 





































