'Carpathian Brigade': The black-shirted Hungary hooligans behind Wembley chaos

With chants citing their own days of empire, Hungary's black-clad Ultras sing from almost the same hymn sheet as the National Front hooligans who blighted the England team in the 1980s.
The driving force for the upturn in trouble, particularly in Budapest, is the Carpathian Brigade, an umbrella group of organised fan groups that came together around 12 years to make their presence felt internationally.
Their black-shirted uniforms are a nod to waves of fascism in the country tracing all the way back to the 1920s, but experts claim not all fan groups who initially signed up were of extremist leanings.
Instead, it is the hardline nationalist politics of Hungary's current Government, and its tacit approval of discriminatory chanting at football, that is said to have radicalised and emboldened the group in recent years.
"The Government has supported the Carpathian Brigade, so they officially sanction what goes on," says Piara Powar, the executive director of the monitoring network Fare, which had observers at Tuesday night’s game at Wembley.
WC Qualification. 12.10.2021
England - Hungary.
Hungarian and Polish fans vs. police. pic.twitter.com/6kyOoc4x5A— HooligansTV (@HooligansTV_eu) October 12, 2021
Fascist fan groups have been attending Hungarian football matches since the 1950s. But reflecting a fresh upturn of nationalism across Eastern Europe, numbers have increased in recent years.
The Carpathian Brigade set up headquarters behind the goal at the Puskas Arena, where they lead hostile chanting to players kneeling for Black Lives Matter and even Uefa's anti-homophobia messages.
Ultra groups also organise demonstrations away from football in support of the hardline anti-immigration politics of nationalist Prime Minister Viktor Orban, who has in turn repeatedly refused to criticise them.
Little contrition can be expected from him or anyone else in Government after gangs run amok against England on the Wembley terraces.
There had been none at all three weeks ago, when Hungary was fined £158,416 and ordered to play behind closed doors by Fifa over abuse against Jude Bellingham and Raheem Sterling in Budapest.
That punishment came on top of a two-match stadium ban followed sanctions already imposed on Hungary by Uefa for racist and homophobic incidents at Euro 2020.
Abuse monitors say the disorder and abuse on the terraces will keep intensifying while the nation's Far Right leadership effectively condones extremist views.
Professor Geoff Pearson, one of Britain’s leading experts on hooliganism and football crowd control, suggests, however, that the 700 away fans who arrived at Wembley may not have come intent on violence.
"I don't think there's any suggestion that the Hungarian Ultras turned up to Wembley with the intention of fighting England fans or clashing with police," said the senior lecturer in criminal law at Manchester University.
"What we've seen here, from the sounds of it, is an intervention, which has been seen as illegitimate by the Hungarian Ultra group and, as a result of that, they have fought back."
Prof Pearson, who was on the ground to observe violence flaring in France at Euro 2016 as well as clashes before then in 1998, said it is "easy to over-exaggerate" how organised fan firms operate. He suggests Hungarian Ultras are less intent on "pre-planned violence" than, for example, the Russian hooligans who ambushed England fans in Marseille five years ago.
"It's unquestionable that those ultra groups following Hungary have a dominant racist narrative," he adds.
"That's not to say that everybody that wears that black shirt and goes into those groups will be racist, but the narrative is dominantly anti-Black Lives Matter, for example, which is quite different with regards to Russia in 2016, where the group was there to engage in disorder, and active violence."
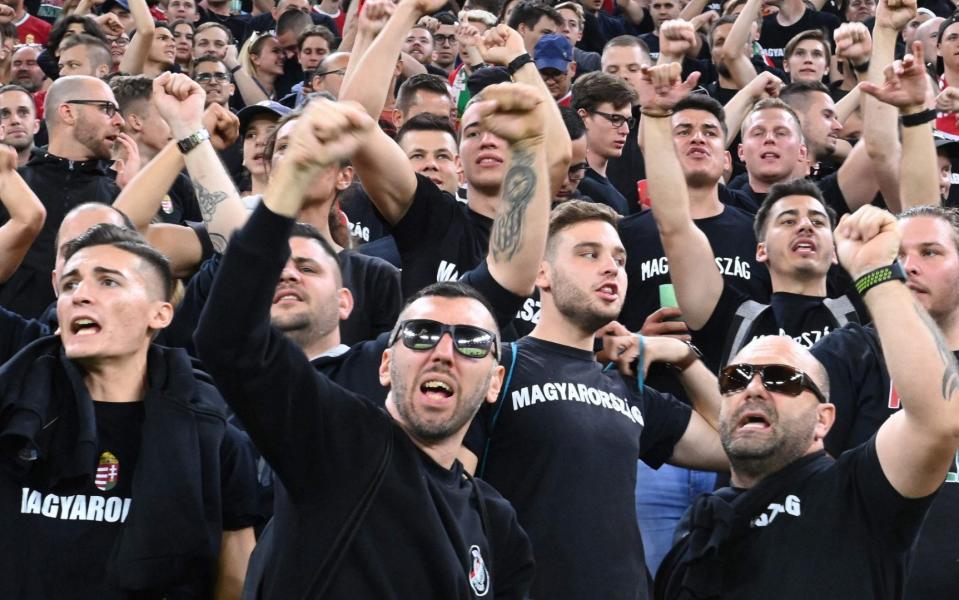

Nevertheless, four of Hungary's previous six games played in front of fans have been blighted with criticism, with either homophobic banners or monkey chanting.
During the opening Euro 2020 game against Portugal, photographs emerged on social media showing group members raising banners and voicing their opposition against the gay community. There were also further demonstrations by the umbrella group outside the stadium ahead of France players taking a knee before kick-off during the second fixture.
A number of French media reports alleged monkey chants were later directed at Paul Pogba, N'Golo Kanté and Kylian Mbappé. Fans had also loudly jeered Republic of Ireland players for taking the knee at a Euro 2020 warm-up game.
That was after the Hungarian football federation said it opposed "unauthorised politics" and Orban accused those performing the gesture of “provocation” and backed those booing it.
Meanwhile, during the fixture against Germany, a section of Hungary supporters were pictured displaying a homophobic banner. Uefa had declined a request to illuminate Munich's Allianz Arena in rainbow colours for Hungary’s match against Germany on the grounds of the gesture having political context.
Neo-Nazi leanings reportedly stretch back at least 50 years in the Hungarian game, particularly at club side Ferencvaros. "Football fan society is basically nationalist in Hungary, and we are proud of that," a representative of the neo-Nazi group Legio Hungaria told Bellingcat in September.
Clashes with police and stewards are also nothing new. In 2013 in Bucharest, Hungarian fans clashed with Romanian riot police after a 3-0 loss. In a Euros qualifier the next year, also in Bucharest, Hungary’s ultras burst through the barriers before the game had started to attack unsuspecting Romanian fans.
There should have been no surprise that Poland fans were mingling with the Ultras at Wembley too. Powar told Telegraph Sport of long-term "alliances" between the nation's fans, with a shared political ideology of "ultra groups" and "far-right" sympathies. "There’s quite a lot of points of convergence," he added.

 Yahoo Sport
Yahoo Sport 





































