All the Reasons Why You May Have Lower Back Pain, According to Doctors
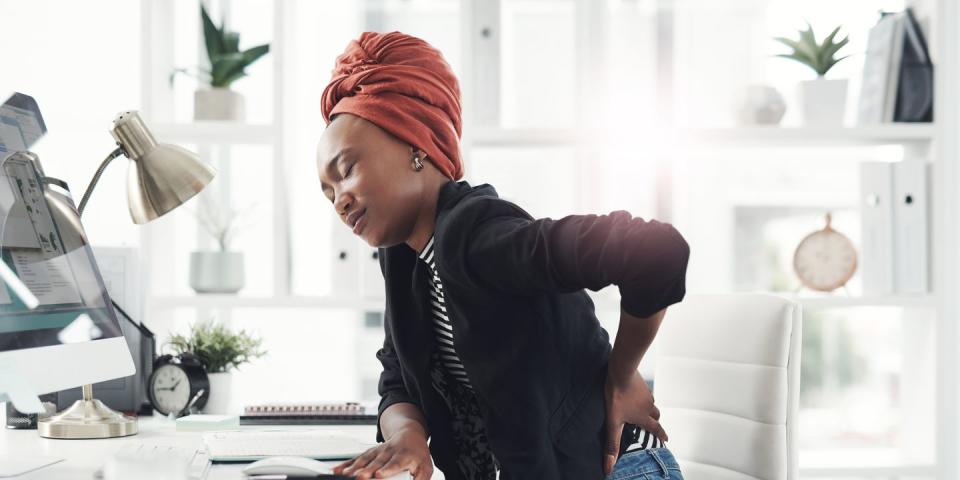

One morning, I just woke up with it: shooting pain and stiffness all round my lower back and no recent injury to account for it. I slowly rolled out of bed and hobbled to work, confused about what was going on in my body. All I knew was that sitting at my desk seemed to be making things worse. I would be groaning out of my seat for days without understanding how to feel better. I was getting worried, and wondered whether or not I needed to see a doctor.
Perhaps you can relate. Looking at the stats, most people have own frustrating tale about lower back pain, or will at some point. It's thought to affect around one-third of the UK adult population – of these, around 20% will ask their GP about it.
One theory as to why this is so common is rooted in our skeletal design, says Dr Bill Rifkin,who overseas guideline development for acute patient care at MCG Health. 'Our evolution wasn’t perfect,' he says. When our quadruped humanoid ancestors developed into upright, walking beings, they started to bear more of their weight in the lumbar region—the second lowest region of the spine.'When you go from four to two legs, you're putting a lot more strain on the lower back,' adds Dr. Rifkin. 'My dog doesn’t get back pain! So for us, the lower back is a vulnerable spot in our bodies just by the mechanics of it.'
The way we move (lift our bags from the floor, bend over to tie our shoes, squat) and the ways we don't move (sit, stand, sleep) often influence our lower back health. There are many muscles, ligaments, and tendons that work together to help move, stabilise, and protect the spine. And the spine itself—which is made up of 24 small bones (vertebrae) that are each cushioned by gel-like cushions called discs—is also comprised of many pieces. So when one of these parts (whether muscular, skeletal, or neurological) is out of whack, you may experience aches, stiffness, numbness, and an inability to do normal, everyday activities.
There are also more serious conditions and illnesses that can trigger lower back soreness. And so with all the various factors that can cause us to bend over in agony, it can be tricky to I.D. the exact root of our pain. Not all back pain is the same. Some cases will heal up on their own, while chronic conditions might need more care and attention.
Common Causes of Lower Back Pain
1. Sedentary Lifestyles
Many of us spend a lot of our waking hours on our keister thanks to jobs that have us in front of computers all day. But unfortunately, such a sedentary lifestyle can increase your risk of chronic low back pain, disability, and mortality, says Dr Stacey Popko, a paediatrician and doctor of general internal medicine. However, the exact reasons as to why this is the case is not obvious.
'There is a lot of interest in better understanding the effects of 'sedentary behaviour' in medicine,' says Dr. Popko. 'And there is not yet clear evidence about what role sedentary behaviour plays in chronic low back pain.'
Some exercise physiologists suggest that it could be the way our muscles are activated (or deactivated) when we are sitting. For example, when our bums remain glued to our seats for too long, we tend to slouch and underutilise the core muscles that support the lower back and decompress the spine.
In my case, I discovered that my hamstrings and glutes had become super tight and cranky from being stuck in the same position from 9-5. Once I figured that out, stretching and frequent walk breaks turned out to be a huge relief.
2. Poor Posture
In a similar vein, poor posture can either cause lower back pain or make it worse. This doesn't only mean slouching or slumping at your desk; poor posture could also include leaning on one leg while you stand, or walking with your bottom so far out you have an arch in your lower back. While these postures aren’t inherently 'poor for a moment in time, maintaining these positions for prolonged periods can increase the strain on the muscles and ligaments around the lumbar spine.
3. Sudden Muscle or Ligament Strain
We’ve all heard the story of our friend who pulled something in their back trying to move the couch. (Maybe this was you.) It's extremely common for people to tweak muscles and ligaments when they are lifting with improper form or moving a load that puts too much tension on the lower back. The risk can increase when a person's muscles are 'deconditioned,; says Dr. Rifkin. This often occurs when someone isn’t very physically active and has lost muscle tone and strength.
4. Muscle Fatigue
In certain instances, back pain isn’t due to lack of activity, but the type of activities we do on a regular basis, says Dr. Popko.
'We see a lot of back pain is related to athletics and some of the jobs that people do,' she adds.
For example, you could have a job that often requires you to lift heavy objects. When you continue to lift over and over without enough rest, the muscles needed to perform the movement may not fire as efficiently, which can lead to faulty mechanics, and potentially injury. The same could be true of anyone who plays a sport that places a lot of torque on the spine.
Rare Causes of Lower Back Pain
5. Bulging or Herniated Disc
The jelly-doughnut-looking cushions between our vertebrae are subject to injury and overall wear and tear. As we age, they dehydrate, become stiff, and sometimes balloon out and irritate neighbouring nerve roots. Traumatic accidents and sudden movements can also put too much pressure on a disc and cause it to rupture, protrude, and create pain. While herniated disc symptoms vary, people can experience shooting pain down their legs.
Just hearing the words 'bulging disc' can sound scary for some people because many assume that it means that they need back surgery. But Dr. Rifkin says this isn’t often the case; in fact, a disc abnormality doesn't always mean trouble.
“Most back pain is not about [herniated disks],” he says. “If you did spine MRIs on 100 patients over the age of 50, many would have disc problems, but no pain. So it is important to realise that surgery is only indicated for a relatively small proportion of back pain.”
6. Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a disorder that causes the spine to curve abnormally. It has no known cause and is not a common source for lower back pain, specifically, but it can play a part.
7. Degenerative Spine Conditions and Autoimmune Diseases
Certain diseases like osteoporosis and osteoarthritis can cause lower back pain. Osteoporosis causes bones to become weak and brittle, potentially leading to fractures in the spine, while osteoarthritis is a progressive joint disease that breaks down protective cartilage. 'There is also back pain that's part of different autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus,' adds Dr. Rifkin, but these are rarer cases.
8. Cancer
Lower back pain in relation to cancer can—in some instances—be caused by a tumour in the lumbar area. 'If you have a history of organ cancer—like breast cancer or prostate cancer — it's still very likely that back pain is not due to metastasis, but it could be,' says Dr. Rifkin.
What to Do If You're Experiencing Back Pain
Here’s some good news: If you’re currently putting up with lower back aches, there’s a good chance that it will heal. 'Most people who have acute low back pain are actually going to get better on their own in six weeks or less,' says Dr. Popko.
Many cases get better with rest and home treatment. 'Try the usual things: heat, if that helps, ice, if that helps—and classes of [anti-inflammatory] drugs like ibuprofen are very, very useful,' says Dr. Rifkin.
It also could help to avoid movements that aggravate the pain, but make sure to stay as active as you can. Prolonged bed rest may make back strains worse as the muscles around the spine begin to weaken and lose tone. You also might want to look into making your work space better for your body's needs and see if that helps.
If your back pain does not resolve within 6-12 weeks, go see your primary care doctor. They may refer you to physical therapy or to an orthopedist. With doctor approval, massage therapy might also be a benefit.
However, before you take a “wait and see” approach, there are also a few red flags you need to be aware of to understand whether or not your back pain might be a more serious issue. If you...
Have back pain associated with serious trauma (like a car accident or a major fall)
Have cancer or have a history of cancer
Have trouble going to the bathroom or can't hold your urine or stool
Are experiencing neurological dysfunction like leg weakness or numbness
Lose sensation around the groin area
Have a fever in associated with your back pain
... it’s best to seek emergency care ASAP.
But again, unless you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, you can take a breath. Try to give your lower back some R&R, and if you're really worried, your GP can guide you on your next best steps.
Cut through the noise and get practical, expert advice, home workouts, easy nutrition and more direct to your inbox. Sign up to the WOMEN'S HEALTH NEWSLETTER.
You Might Also Like

 Yahoo Sport
Yahoo Sport 






































